Deploy a Spring Boot application to Cloud Foundry with GitLab CI/CD
Introduction
This article demonstrates how to use the Continuous Deployment method to deploy a Spring Boot application to Cloud Foundry (CF) with GitLab CI/CD.
All the code for this project can be found in this GitLab repository.
In case you're interested in deploying Spring Boot applications to Kubernetes using GitLab CI/CD, read through the blog post Continuous Delivery of a Spring Boot application with GitLab CI and Kubernetes.
Requirements
This tutorial assumes you are familiar with Java, GitLab, Cloud Foundry, and GitLab CI/CD.
To follow along, you need:
- An account on Pivotal Web Services (PWS) or any other Cloud Foundry (CF) instance.
- An account on GitLab.
NOTE:
If you're not deploying to PWS, you must replace the api.run.pivotal.io URL in all the below
commands with the API URL
of your CF instance.
Create your project
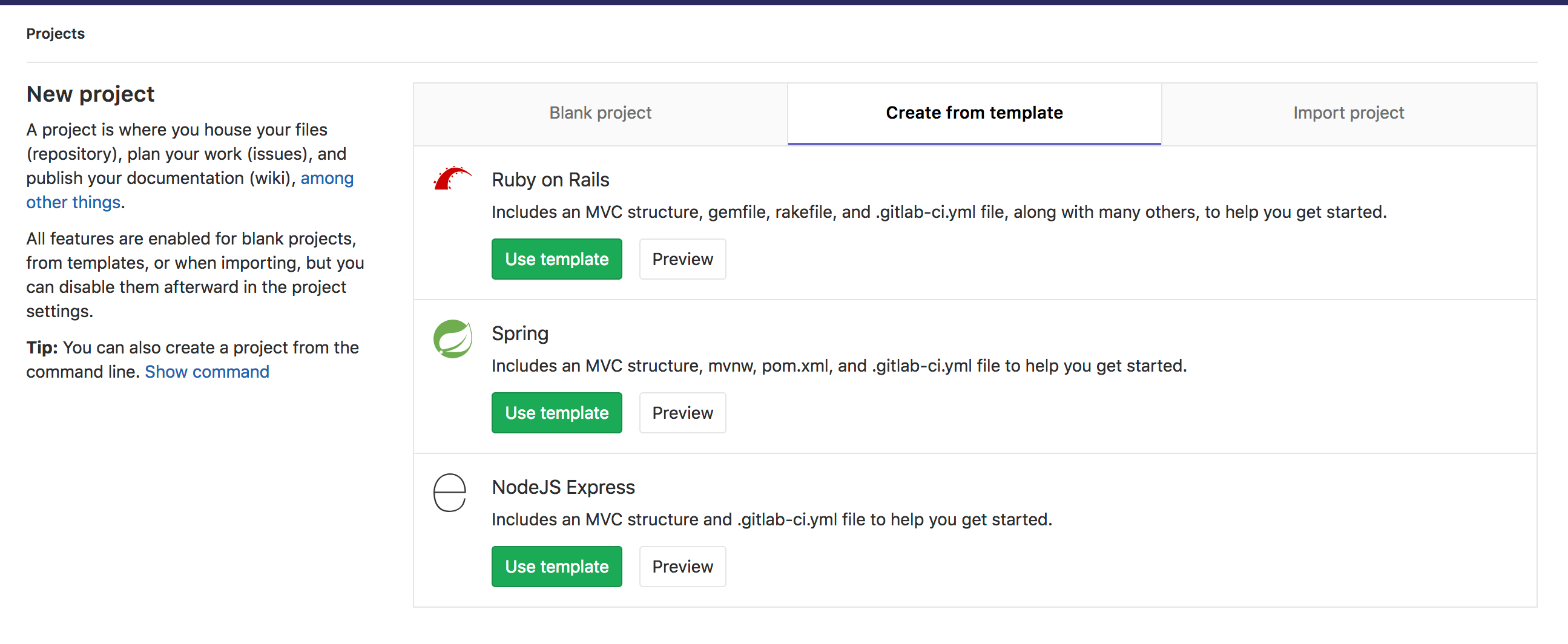
To create your Spring Boot application you can use the Spring template in GitLab when creating a new project:
Configure the deployment to Cloud Foundry
To deploy to Cloud Foundry you must add a manifest.yml file. This
is the configuration for the CF CLI you must use to deploy the application.
Create this in the root directory of your project with the following
content:
---
applications:
- name: gitlab-hello-world
random-route: true
memory: 1G
path: target/demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarConfigure GitLab CI/CD to deploy your application
Now you must add the GitLab CI/CD configuration file
(.gitlab-ci.yml)
to your project's root. This is how GitLab figures out what commands must run whenever
code is pushed to your repository. Add the following .gitlab-ci.yml
file to the root directory of the repository. GitLab detects it
automatically and runs the defined steps once you push your code:
image: java:8
stages:
- build
- deploy
before_script:
- chmod +x mvnw
build:
stage: build
script: ./mvnw package
artifacts:
paths:
- target/demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
production:
stage: deploy
script:
- curl --location "https://cli.run.pivotal.io/stable?release=linux64-binary&source=github" | tar zx
- ./cf login -u $CF_USERNAME -p $CF_PASSWORD -a api.run.pivotal.io
- ./cf push
only:
- masterThis uses the java:8 Docker image
to build your application, as it provides the up-to-date Java 8 JDK on Docker Hub.
You also added the only clause
to ensure your deployments only happen when you push to the master branch.
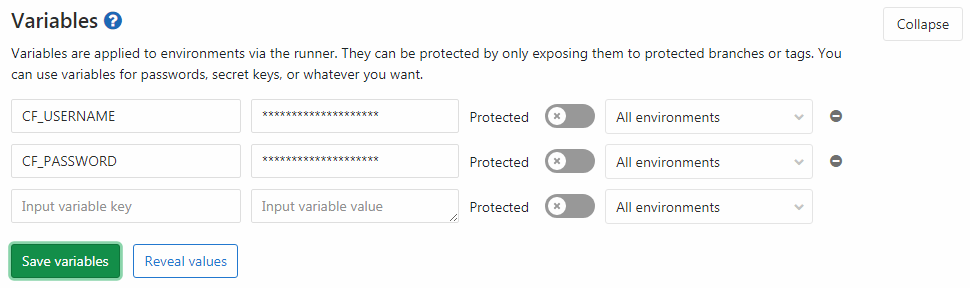
Because the steps defined in .gitlab-ci.yml require credentials to sign in to
CF, you must add your CF credentials as
environment variables
in GitLab CI/CD. To set the environment variables, navigate to your project's
Settings > CI/CD, and then expand Variables. Name the variables
CF_USERNAME and CF_PASSWORD and set them to the correct values.
After set up, GitLab CI/CD deploys your app to CF at every push to your repository's default branch. To review the build logs or watch your builds running live, navigate to CI/CD > Pipelines.
WARNING: It's considered best practice for security to create a separate deploy user for your application and add its credentials to GitLab instead of using a developer's credentials.
To start a manual deployment in GitLab go to CI/CD > Pipelines then click
Run Pipeline. After the app is finished deploying, it displays the
URL of your application in the logs for the production job:
requested state: started
instances: 1/1
usage: 1G x 1 instances
urls: gitlab-hello-world-undissembling-hotchpot.cfapps.io
last uploaded: Mon Nov 6 10:02:25 UTC 2017
stack: cflinuxfs2
buildpack: client-certificate-mapper=1.2.0_RELEASE container-security-provider=1.8.0_RELEASE java-buildpack=v4.5-offline-https://github.com/cloudfoundry/java-buildpack.git#ffeefb9 java-main java-opts jvmkill-agent=1.10.0_RELEASE open-jdk-like-jre=1.8.0_1...
state since cpu memory disk details
#0 running 2017-11-06 09:03:22 PM 120.4% 291.9M of 1G 137.6M of 1GYou can then visit your deployed application (for this example,
https://gitlab-hello-world-undissembling-hotchpot.cfapps.io/) and you should
see the "Spring is here!" message.