Gitpod Integration
- Introduced in GitLab 13.4.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 13.8
With Gitpod you can describe your dev environment as code to get fully set up, compiled, and tested dev environments for any GitLab project. The dev environments are not only automated but also prebuilt which means that Gitpod continuously builds your Git branches like a CI server. By that you don’t have to wait for dependencies to be downloaded and builds to finish, but you can start coding immediately.
In short: With Gitpod you can start coding instantly on any project, branch, and merge request from any device, at any time.
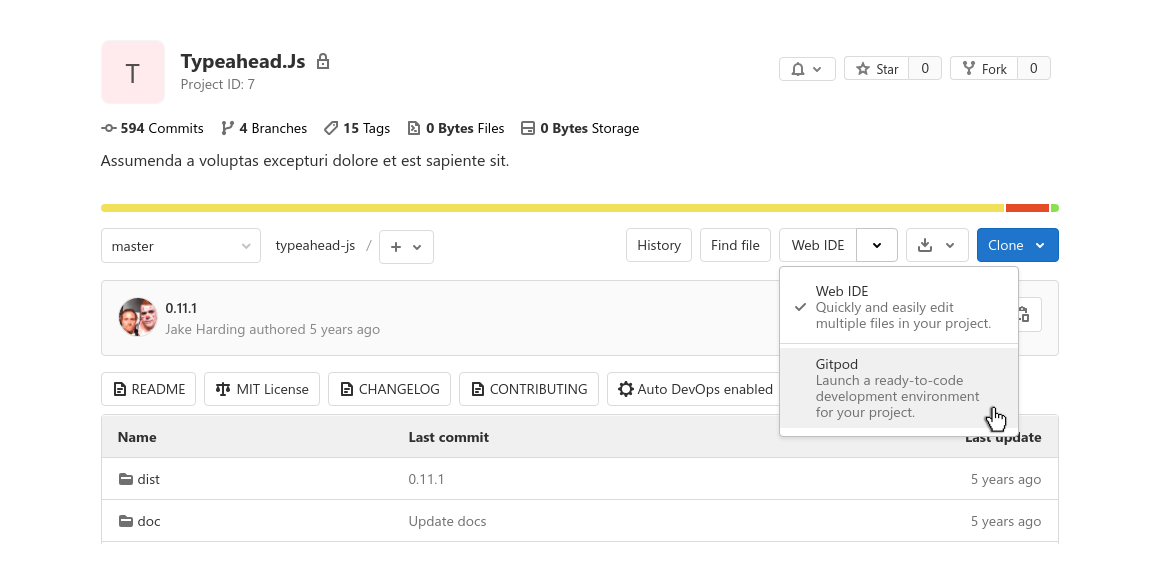
You can launch Gitpod directly from GitLab by clicking the Gitpod button from the Web IDE dropdown on the project page:
To learn more about Gitpod, see their features and documentation.
To use the GitLab-Gitpod integration, you need to enable it from your user preferences:
- From the GitLab UI, click your avatar in the top-right corner, then click Settings.
- On the left-hand nav, click Preferences.
- Under Integrations, find the Gitpod section.
- Check Enable Gitpod.
Users of GitLab.com can enable it and start using straightaway. Users of GitLab self-managed instances can follow the same steps once the integration has been enabled and configured by a GitLab administrator.
Configure your GitLab instance with Gitpod (CORE ONLY)
The integration of Gitpod with GitLab is enabled on GitLab.com and available to all users. For GitLab self-managed instances, a GitLab administrator needs to enable it through the admin settings.
First, you (GitLab admin) need to set up a Gitpod instance to integrate with GitLab. Head over to the Gitpod documentation to get your instance up and running. Once done:
- In GitLab, go to Admin Area > Settings > General.
- Expand the Gitpod configuration section.
- Check Enable Gitpod.
- Add your Gitpod instance URL (for example,
https://gitpod.example.com).